Latest Advancements In Defense And Aerospace Systems Globally

A substantial disruption is being experienced by the global aerospace and defense business landscape, driven by a keen focus on innovation and digital transformation, and geopolitical situations. The increasing number of passengers, leads to the growth of commercial aerospace, which in turn is leading to expansion initiatives. Research estimates that 38,000 aircrafts are expected to be produced globally in the next two decades. The natural recapitalization cycles, rising geopolitical tensions, greater high/low mix of assets, increased demand for affordable, off-the-shelf equipment, focus on aligning solutions to local requirements, all these factors drive the growth in the defense sector. Moreover, the recent recovery in defense budgets of major economies is expected to push the growth of the defense industry in 2019 and beyond. The aerospace and defense industry is likely to experience the following trends in 2019.
Advancements In Defense Systems
A) DRONES

The drones are essentially flying robots. With over 11,000 such vehicles, the U.S appears to be leading the way. But, as it becomes more affordable, the technology is widely spreading. Reportedly, the advanced drone technology is even possessed by North Korea. Moreover, to spy on and eliminate rivals, off-the-shelf-quad copter drones are already used by narcotics gangs.
B) AUTONOMOUS WEAPONS

Drone technology combined with artificial intelligence is the so-called autonomous weapons. Based on pre-defined criteria and human intervention, these weapons can engage and select targets. After gunpowder and nuclear, these have been potentially called the third revolution in warfare . So far, the current technology is advanced enough. For e.g. an armed quad copter uses facial recognition software to identify targets from a database and open fire.
| Also Read: Aerospace Defence: Advancements in Aircraft and Missiles |
C) WEARABLE DEVICES
With current technology already allowing a human to carry loads of around 90kg without difficulty and spying, the possible military uses here include tracking bodily functions to optimize health and performance, sensing moods to avoid poor decision making, exoskeletons to enhance soldiers performance.
D) ADDITIVE MANUFACTURING
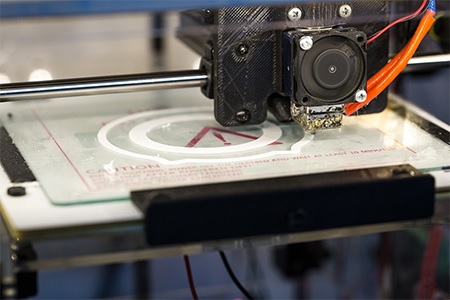
Both US and Chinese armies have already tested 3D printing in war games, and by enabling replacement parts to be manufactured in the field, from locally available materials and digitally transmitted designs, it could revolutionize supply chains. For those injured in service, militaries are even aiming to be able to print skin, food and prosthetics. However, few questions remain to be solved around quality control, intellectual property and liability. There's also a risk of proliferation of certain types of weapon systems, as it becomes easier to bypass normal restrictions such as export controls and copy critical technologies. With greater control of particle size and direction on detonation, the development of new kinds of warhead could be enabled with additive manufacturing.
E) RENEWABLE ENERGY

The development of solar technologies, including dye-sensitized light harvesting materials, which can harness light energy outside the visible spectrum, are already at the forefront by militaries. Another significant method of energy generation is by embedding nano-materials in clothes.
F) NANOTECHNOLOGY
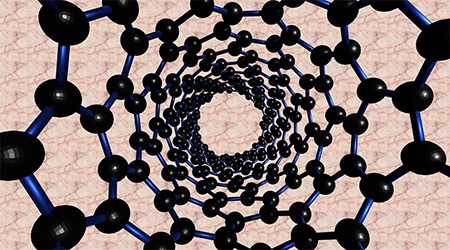
In the last decade, our ability to manipulate particles at the nano scale has progressed significantly, and to make meta materials, which have properties that do not occur naturally, we are rapidly developing technology. The related innovations promise to make weaponry lighter, more mobile, better, smarter and more precise. The two challenges would be - nano electronics need vast amounts of power, and another would be the proliferation of nano weapons, which would be harder to monitor.
G) BIOLOGICAL WEAPONS

The rapid advancements in genetics, biotechnology and genomics are opening up highly lethal and new avenues for the creation of new biological weapons. Engineered superbugs, airborne designer viruses, and genetically modified plagues all seem like potential doomsday scenarios.
H) BIO CHEMICAL WEAPONS

In warfare situations, any usage of chemicals, including non-lethal chemicals are prohibited by the Chemical Weapons Convention. But, with technological advances, such weapons are made into "do-it-yourself" project and increasingly hard to regulate. In the battlefield, new and effective ways of delivering chemical agents are offered by unmanned vehicles. There's an increasing possibility to alter behavioral patterns and emotions with advances in neurobiology and pharmaceuticals.
Advancements In Aerospace Systems
A) ZERO- FUEL AIRCRAFT

A lot of traction has been recently gained by the idea of a zero-fuel aircraft, recently in both civil and commercial sectors. The concept can be used in aerial photography, agriculture, wildlife protection, 3D mapping and the provision of internet access in remote places. According to a lead analyst for aerospace research, photovoltaic panels are used by zero-fuel aircraft to utilize solar energy, to provide necessary force to the engines. A solar-powered prototype, the Solar Impulse 2, had reinforced structural components made out of nano carbon fiber, to reduce the overall weight of the body. To create a long-term development strategy for the zero-fuel aircraft concept and drive market growth, the recent surge in interest has put pressure on global defense and aerospace industries.
B) STRUCTURAL HEALTH MONITORING
To enhance our ability to determine and analyze the status of an aircraft, advanced health management systems - such as prognostics, monitoring and self healing are being developed. Previously, this technology was used onboard an Air France jet that crashed in 2009 to notify headquarters of electrical problems. Presently, it's being used by Boeing and Airbus.
C) ADVANCED SPACE PROPULSION TECHNOLOGIES
For several years now, NASA along with the Department of Energy and the Oak Ridge National Laboratory, have developed a new plasma-based rocket propulsion technology, by the name, VASIMR® rocket (Variable Specific Impulse Magnetoplasma Rocket). This new technology is expected to enable long-term space missions and reduce fuel consumption.
D) ADVANCED MATERIALS

Aircraft manufacturers are gaining huge benefit with advance in material science. The airplane wings have become more efficient by reducing fuel and weight consumption with the help of new materials like carbon nano tubes and graphene. A morphing wing has been developed by scientists, using these new materials.
E) SMART AUTOMATION AND BLOCK CHAIN

What do you think is the highly specialized and complicated process in aerospace. It's none other than manufacturing aircrafts. However, new processes and technologies are making it simpler and faster.
Defense as well as aerospace companies are also starting to explore the digital realm. Among supply chain partners, technologies such as block chain are helping to automate transactions and improve transparency.
F) 3D PRINTING

In recent years, 3D printing has turned out to be a solution for companies that have had trouble keeping up with production deadlines.
As aerospace companies look for niche suppliers to help expand their supply chain, manufacturing processes and innovative technologies are being developed on a seemingly constant basis and small to medium sized manufacturers are reaping the benefits. As these emerging markets start to compete on a global scale, more and more joint ventures and outsourcing are expected to occur in the next five to ten years.










